Vicuna-13B, launched recently, is an open-source chatbot that has been trained by fine-tuning LLaMA on user-shared conversations collected from ShareGPT. Vicuna-13B performs exceptionally well with over 90%* quality, surpassing models like LLaMA and Stanford Alpaca while achieving the same quality as OpenAI ChatGPT and Google Bard. The cost of training Vicuna-13B is approximately $300, and the code, weights, and online demo are publicly available for non-commercial use.
As per their website, when it comes to performance, Vicuna-13B has been fine-tuned using 70K user-shared ChatGPT conversations. As a result, it can produce detailed and well-structured answers that are superior to those of Alpaca. With the recent advancements in GPT-4, it can produce highly consistent ranks and detailed assessments when comparing chatbots' responses. Preliminary evaluations based on GPT-4, have shown that Vicuna-13B achieves over 90%* capability of Bard/ChatGPT.
Workflow Overview:
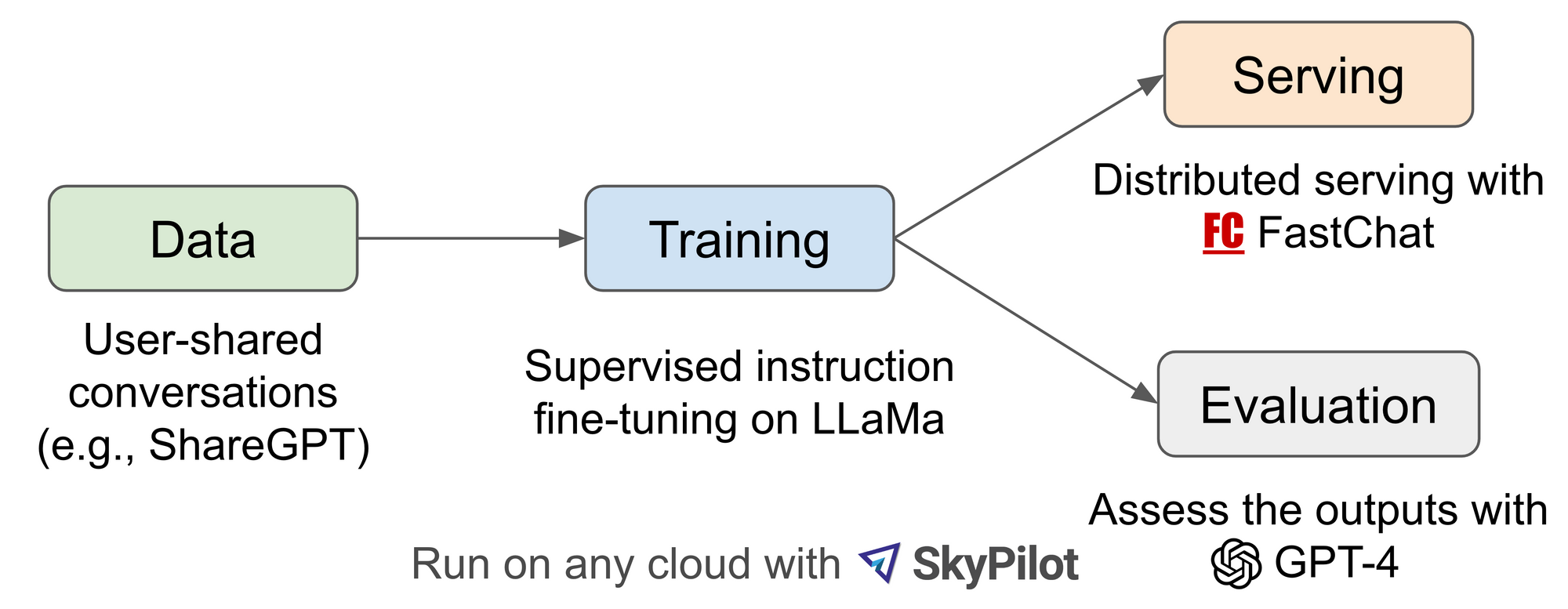
Inspired by the Meta LLaMA and Stanford Alpaca project, Vicuna-13B is an open-source chatbot backed by an enhanced dataset and an easy-to-use, scalable infrastructure.
By fine-tuning a LLaMA base model on user-shared conversations collected from ShareGPT.com, Vicuna-13B has demonstrated competitive performance compared to other open-source models like Stanford Alpaca.
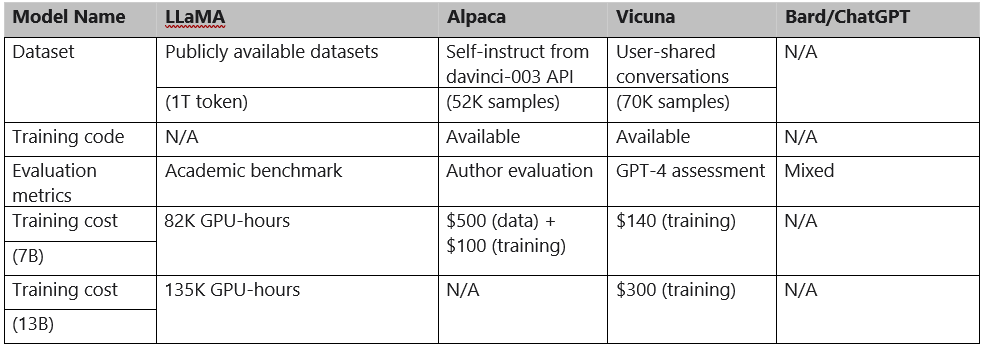
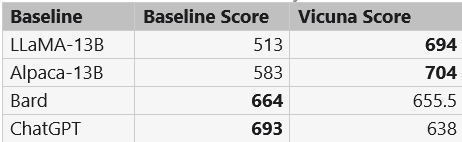
A detailed comparison of LLaMA, Alpaca, ChatGPT, and Vicuna is shown in Table 1 below.
How To evaluate a Chatbot:
Chatbot evaluation is a complex task as it requires assessing various aspects of a chatbot's performance, including language understanding, reasoning, and context awareness. With the advancement of AI chatbots, existing benchmarks may no longer suffice.
For example, the evaluation dataset used in Stanford's Alpaca can be effectively answered by state-of-the-art chatbots, making it difficult for humans to differentiate between their performances. Furthermore, training and testing data contamination and the potentially high cost of creating new benchmarks pose additional challenges. To address these issues, Large Model Systems Organization (LMSYS Org) proposed an evaluation framework based on GPT-4 to automate chatbot performance assessment.
To implement the evaluation framework, eight question categories were identified such as Fermi problems, roleplay scenarios, and coding/math tasks that test different aspects of a chatbot's performance. By crafting diverse and challenging questions through prompt engineering, GPT-4 generated ten questions per category, and answers from five chatbots were collected, including LLaMA, Alpaca, ChatGPT, Bard, and Vicuna. GPT-4 then rated the quality of the answers based on helpfulness, relevance, accuracy, and detail.
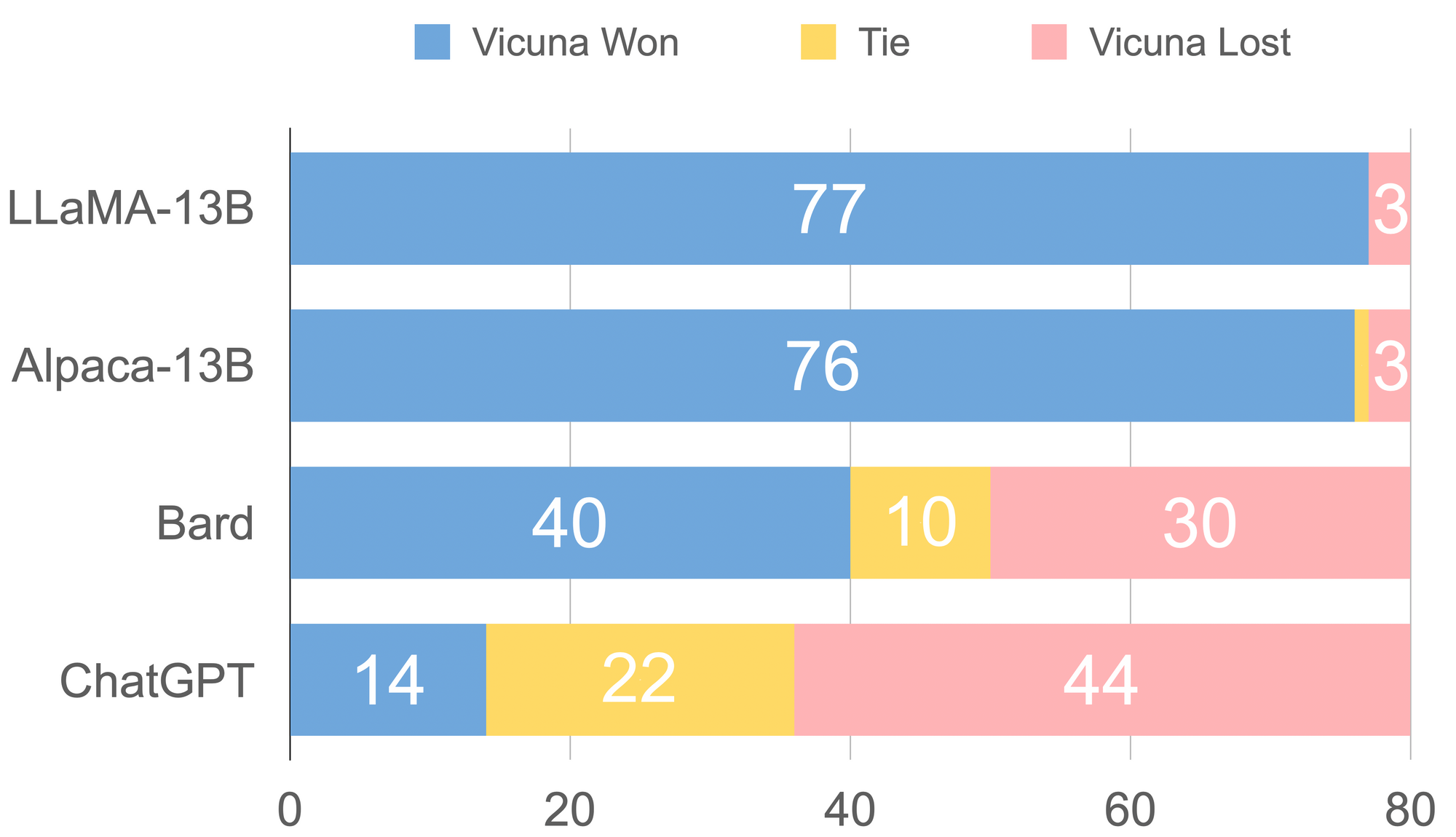
Figure 3. Response Comparison Assessed by GPT-4
In Figure 3, there is a comparison between all the baselines and Vicuna, showing that GPT-4 prefers Vicuna over state-of-the-art open-source models like LLaMA and Alpaca in more than 90% of the questions. Furthermore, it achieves competitive performance against proprietary models like ChatGPT and Bard. GPT-4 rates Vicuna's response as better or equal to ChatGPT's in 45% of the questions. The total score for each comparison pair of Vicuna with other models can be calculated by adding up the scores obtained by each model on 80 questions, and Vicuna's total score is 92% of ChatGPT's, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 : Total Scores Assessed by GPT-4
Despite the recent advancements, chatbots still face limitations. For example, they may struggle with basic math problems or have limited coding ability. As AI chatbots become more advanced, current open benchmarks may not be sufficient to evaluate their performance accurately. Our proposed evaluation framework based on GPT-4 has the potential to automate chatbot performance assessment, but it is not yet a rigorous approach. Therefore, building a robust and comprehensive evaluation system for chatbots remains an open question that requires further research.
Limitations
Vicuna, like other large language models, has some limitations. It struggles with tasks involving reasoning and mathematics, and it may not always provide completely accurate information. Furthermore, it has not been optimized to ensure safety or mitigate potential toxicity or bias. However, we use the OpenAI moderation API to filter out inappropriate user inputs in our online demo to address safety concerns. Despite these limitations, we believe that Vicuna can be a useful starting point for future research to improve its capabilities.

We research, curate and publish daily updates from the field of AI. Paid subscription gives you access to paid articles, a platform to build your own generative AI tools, invitations to closed events and open-source tools.
Consider becoming a paying subscriber to get the latest!